Project Category : Predictive Modeling
Sundre Forest Products Computer Model
Enable Sundre Forest Products to predict areas within their FMA in which Historical Resources Impact Assessment costs are likely, so that they can be avoided, by developing a predictive computer model based on known sites.
The Task
Enable Sundre Forest Products to predict areas within their FMA in which Historical Resources Impact Assessment costs are likely, so that they can be avoided, by developing a predictive computer model based on known sites.
Special Considerations
An unique and exciting aspect Sundre Forest Products Inc. Forest Management Area (FMA) is the availability of extremely high resolution LiDAR elevation data. We also had detailed site data for about 200 known historical sites within the modelling area. Finally, the area to be modelled was huge; the FMA is about 553,000 ha (5,530 km2). This all translates into large files and long computational times.

Our Solution
We followed the best practices of model building by dividing our known sites into testing and training sets. We used the training set to build the model and then we tested its predictive power by seeing how many of the known sites in the testing set the model could predict on its own.
We decided to build our model with 10 meter by 10 meter cells. Given the accuracy of the LiDAR data we thought we could really capture some fine features in the model that would be lost with 30 or 60 meter grids. This decision resulted in over 141 million cells for each variable and very time consuming computations!
Many modellers use multiple regression to make predictions but it is not an ideal method for modelling because it assumes all of the input variables are independent. Many modellers ignore this important assumption and use multiple regression anyway even though they know their input variables are not independent. We decided to take advantage of some exciting tools from the field of machine learning and employ a “support vector machine” algorithm to make our predictions. One major advantage of support vector machines is that they do not require or assume the inputs are independent. The other advantage of using a support vector machine is that it makes really accurate predictions with our data.
As part of the modelling process, we started with over 25 independent variables that we thought would help us predict the location of unknown sites. And as the model evolved, we removed variables that didn’t help predict sites.
Our model met its performance goals after only one month of development. We decided to assess it’s performance during the following field seasons and make refinements as necessary.
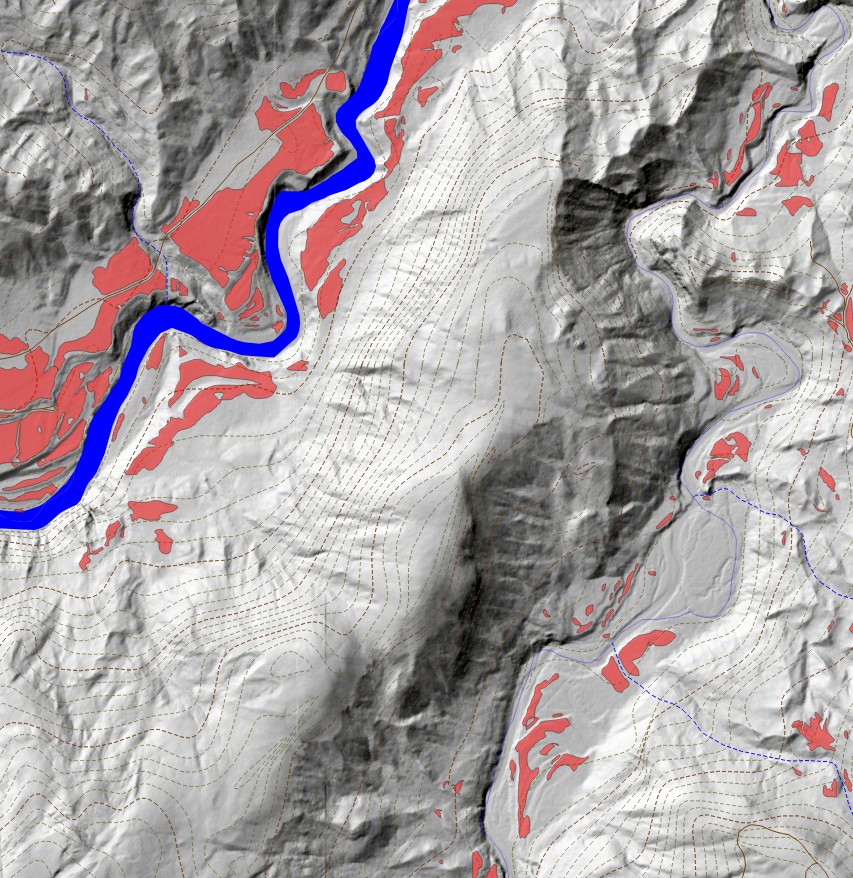
Results
Our final model covers 10% of the land area and is able to predict unknown sites (from the testing set) at 80% accuracy.
The 10 meter cell size and the high-resolution LiDAR data helped us build a model that picks out areas of high potential for containing historical resources without blanketing huge areas of the map as high potential.
While the model does like to predict high potential areas near major streams, it doesn’t just blanket everything within x meters of water as high potential. Our model is much more nuanced than that. It takes slope, solar irradiation, vertical distance to water, local terrain roughness, and several other factors into account when making its predictions.
We delivered a binary predictive model to Sundre Forest Products (the cell is either high potential or not). But our software actually produces continuous predictions from 0 to 100%. A skilled and experienced archaeologist such as Kurtis can use this additional information to make very fine-grained decisions while making assessments to reduce costs for our client.
Sundre Forest Products began using our model in the summer of 2011 to guide decision making and reduce costs associated with actual archaeological field testing and assessment.
This model is just a one step in Sundre Forest Products’ quest to reduce costs associated with archaeology. They plan to have us refine the model in an iterative fashion as we discover more sites, the performance of computer hardware improves, and modelling techniques advance and mature.



